It’s always reassuring for website admins to know they have full control, even while letting others work on the various aspects of the website. But for this to happen, there needs to be a form of boundary that keeps everyone in check.
Now, it is also important to allow other users on the website to do their tasks without the need for daily admin input. This is where WordPress user roles and capabilities are helpful. These will define what each logged-in user can do.
We will explore the various user roles and capabilities in WordPress and why you should make use of them.
Why Do You Need to Define WordPress User Roles and Capabilities
If we take a look at all the websites in different categories and keep aside their traffic, user engagement, and so on, they all share another common factor. It is that all of them see a lot of effort and time invested by numerous people to maintain the website.
This is where trust issues emerge for website owners. Firstly, you want to see the website progress, but at the same time, you want to make sure that the users with backend access don’t go around poking where they shouldn’t be.
For example, in WordPress, if you have a user who is a guest writer, you would never want that user to install or deactivate a plugin or change the theme, would you?
This is where the user roles and capabilities in WordPress are useful. The user roles and capabilities refer to what the users who have access to the dashboard are able to do once logged in. There are two parts to it:
- The user role
- The capability
By default, there are six default user roles, which predefine what the logged user can do. Now, what the users can do with the dashboard once they are logged in is referred to as the capability.
Also read: A Comprehensive Guide on Creating WordPress Custom Post Types
The Six Default WordPress User Roles and Their Capabilities
Now that we have covered what the user roles and capabilities mean in WordPress, it’s time to look at the six default ones in detail.
1. Super Admin
This user role in WordPress is only available when you have a multisite. As a result, the capabilities the super admin user has is stretched over to all the sites they manage. Now, in a multisite network, it is the super admins that can install plugins and themes and control all the other users.
The super admins can assign users with admin roles to the multisites they manage. However, these admins do not have the authority to install new themes or plugins; they can only decide to activate or deactivate the ones they have installed already.
This is what the dashboard of a super admin looks like.
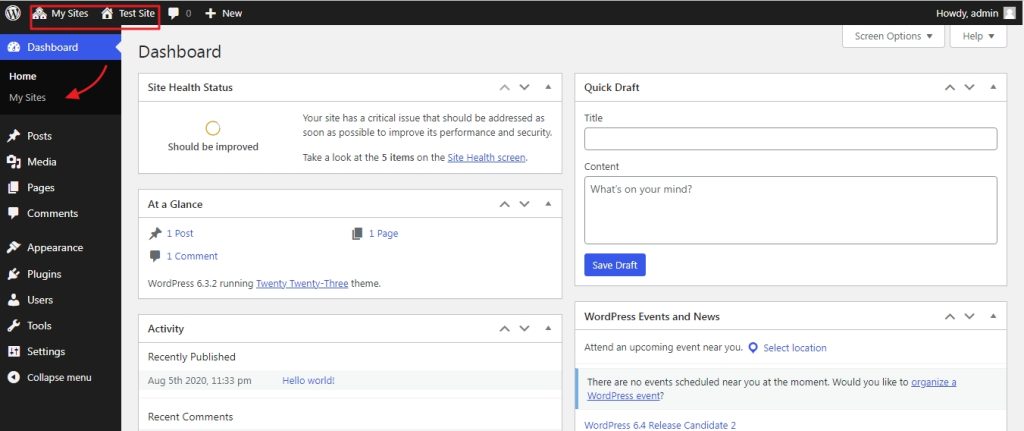
If we select the ‘my sites’ option from the left-hand sidebar, we can view all the sites in the multisite that the super admin manages.
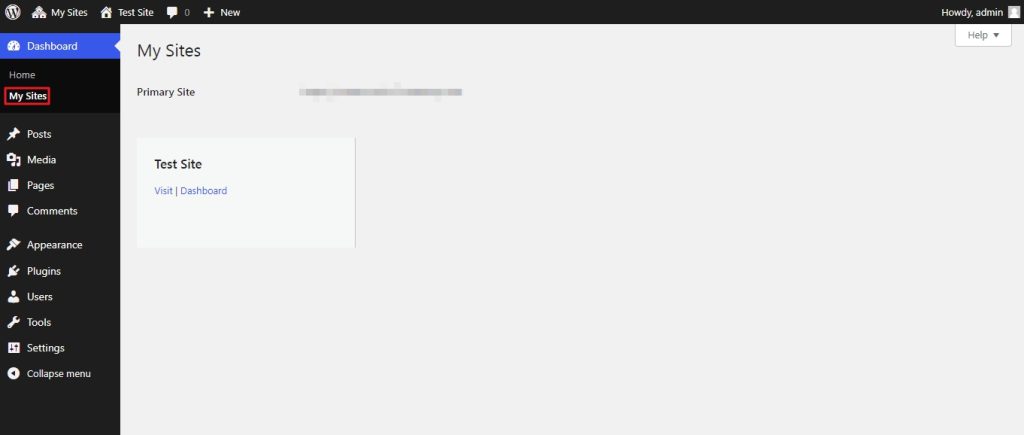
2. Administrator
As long as you are not on a multisite network, the administrator user role sits at the top. As the name suggests, being an administrator, the user has unrestricted and unparalleled capabilities when logged in. Basically, this allows the admin user to pretty much do everything from the dashboard once logged in.
The administrator user role allows full access to the various settings that the dashboard provides, which the other user roles will miss out on. In the below image, take a proper look at the left-hand sidebar. There are various menu options that won’t be available in other user roles.
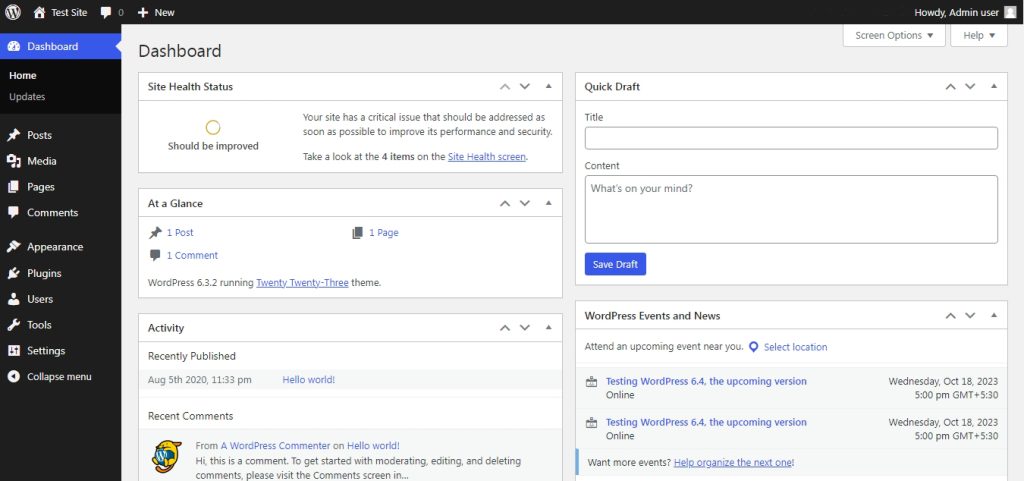
A few of the capabilities of the administrator user role are:
- Create and remove users
- Install and deactivate plugins
- Change theme
- Add and remove pages
- Create and edit patterns
- Upload files
- Create and remove users
These are just a few; the list goes on. So, in short, the administrator role has everything you need to do to maintain a website.
3. Editor
Now, managing everything on the site, including the content, on a day-to-day basis is too much for administrators. It’s not like the admins cannot manage it, but if they focus on the content too much, other areas that need their supervision will take a back seat momentarily. This is where the editor user role comes into play
If there is a user who has complete content management authority on the website, apart from the admin user, it would be a user with the Editor role. This user is essentially the content lead, with the capability to modify posts, pages, and content created by all other users.
The capability of a user with the editor role is solely tied to the content and nothing else. A few of the capabilities of the editor role are:
- Edit pages, posts
- Delete pages, posts
- Moderate comments
- Create, edit, and delete patterns
As you can see from the image below, the dashboard is different. There are various settings on the left-hand sidebar that are not available as compared to an admin role.

As a user with an editor role is concerned with the content aspect, the settings related to installing and deactivating plugins, themes, and other ones are unavailable.
4. Author
Producing content on a wide range of topics is now necessary to cater to a wider group. To achieve this, you need to spend time researching and then get to the actual writing process. The more users you have who focus on content creation, the quicker you can publish new posts.
This brings us to the author user role. Users assigned this role also focus on content like those with the editor role but with more restrictions. The key distinction is their inability to alter content created by other users along with the inability to create and edit pages.
The below image shows the dashboard of a user with the author role and how different it is compared to the editor role.
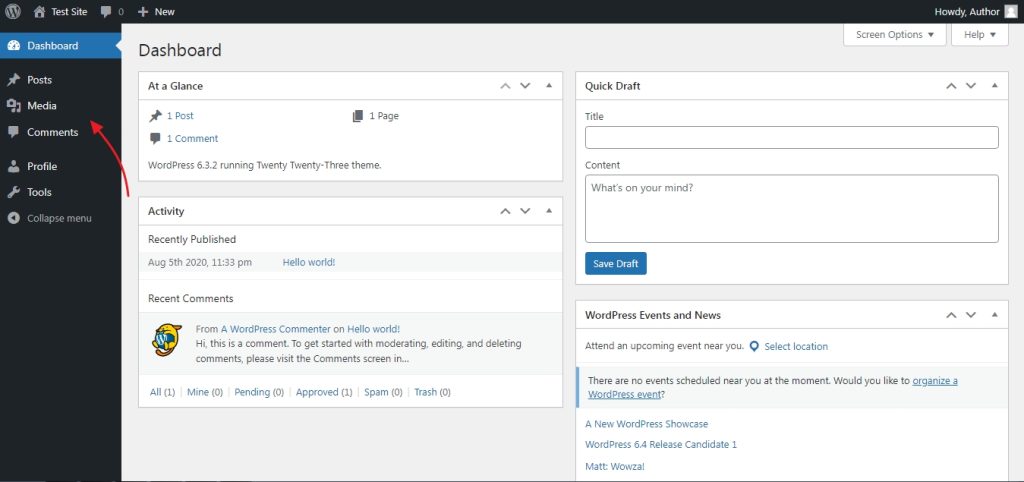
The capabilities of users with author roles are:
- Create, edit, publish, or delete their own posts
- Upload files
- Create, edit, and delete their own patterns
5. Contributor
If you don’t want an author on your site to start a controversy or spread misinformation, or they just need supervision during their training period, then assign them the contributor role. What users can achieve with this role once logged in is very minimal.
The users assigned contributor roles can create posts but cannot upload any media files and cannot publish the posts, but only save them as a draft. The decision to publish the post will be taken either by a user with the editor role or the admin.
But once the post goes live, they won’t be able to edit it but can read the comments on it without the ability to moderate them. Also, they cannot create pages, nor edit other users’ content.
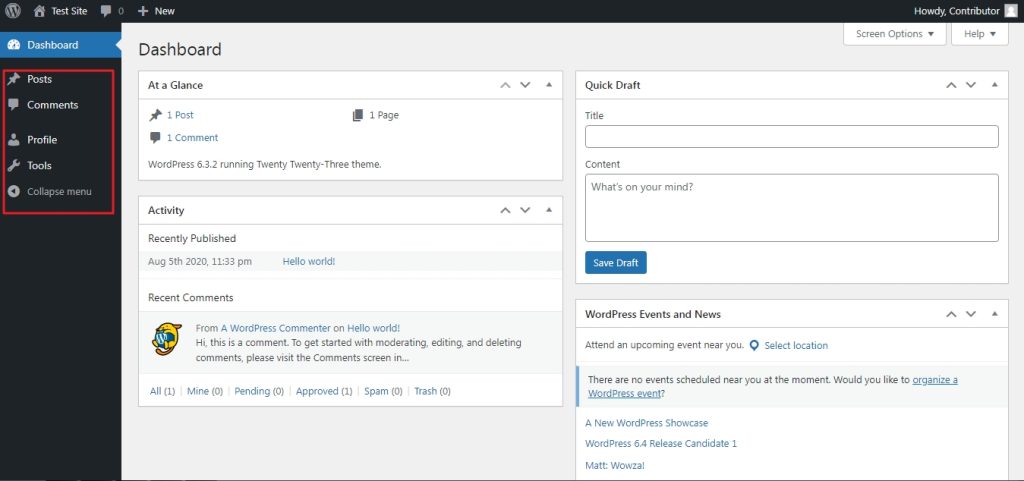
The capabilities of a user with a contributor role are:
- Edit and delete their own post
- Read all posts
- Read patterns
6. Subscriber role
Till now all the user roles we have mentioned have got a varying level of access that deals with content creation. But the users with subscriber roles have nothing to do with the content, in the sense that they cannot create, edit, or add new content as a draft to be reviewed.
The subscriber role in WordPress is suitable for your website visitors. A website admin can determine that in order to leave a comment to start a discussion or even to take part in one, a user needs to sign up. Once a user signs up, they will be assigned the subscriber role.
The capabilities of this role are minimal, as the user can only edit his profile details, and password and add a comment. That’s pretty much it. Also, this user role can also be used to provide access to private content that needs a sign-up from users.
Also read: How To Provide Temporary Admin Access to Your WordPress Site for Support
How to Create New User Roles in WordPress
Now in order for you to create a new user or manage the existing ones, you need to be an admin.
First, access the ‘users’ option from the left-hand sidebar.
Then click on the ‘Add New’.
On the next screen enter the details for the new user and select which role you want to assign. After you have entered all the details, click on ‘Add New User’.
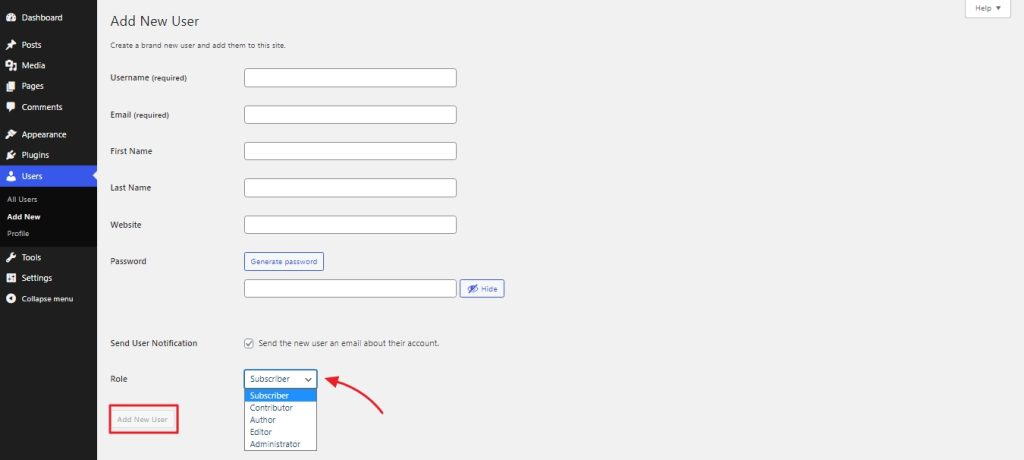
After the user is created, you can view it from the ‘users’ option.
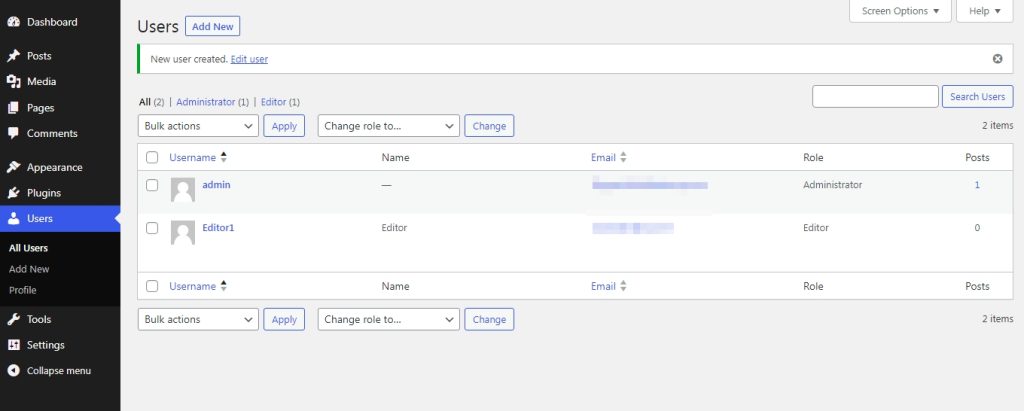
How to Manage Existing WordPress User Roles
Now that we have learned how to create a new user role, it’s time to look at how to manage them. There may come a time when you have to send a password reset or change their user role and so on.
In order to do this, head over to the ‘users’ section and hover the mouse over the user to whom you wish to make changes. This will show the option that we are looking for.
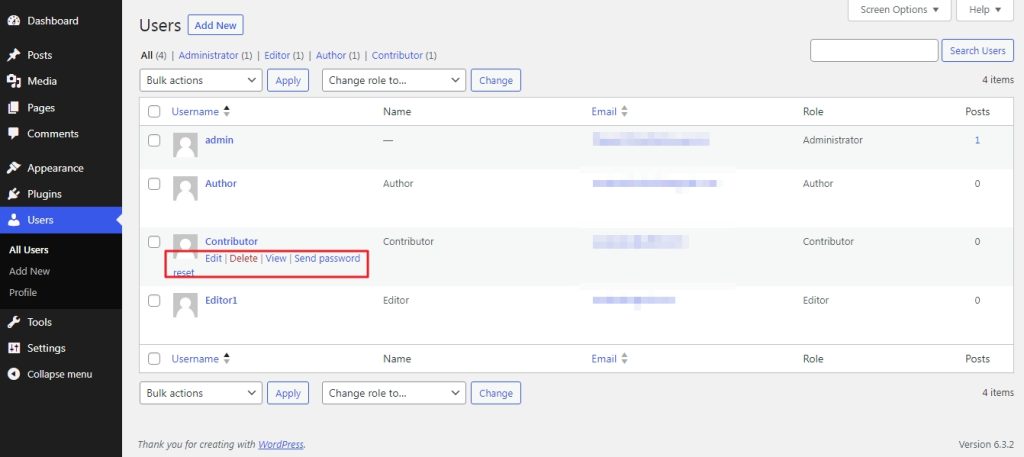
Now click on ‘Edit’, which will bring us to this page. From here we can change the user role if we wish to.
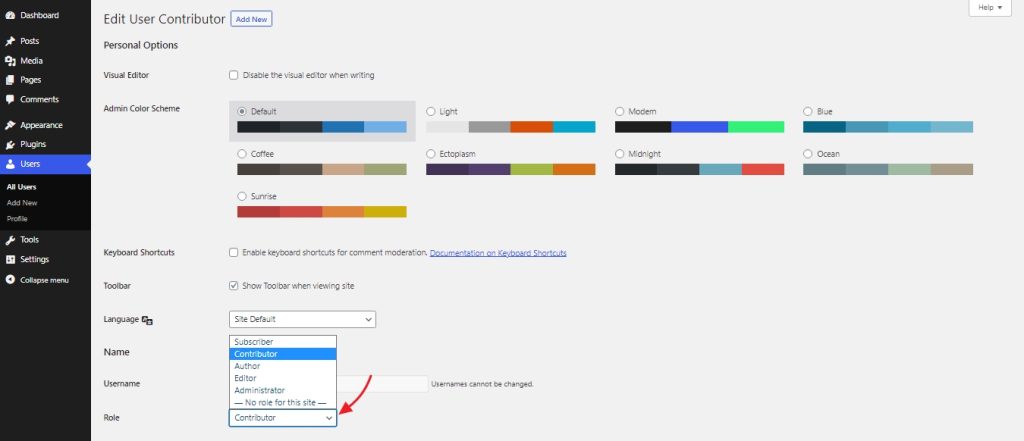
We can also update the details such as the name and profile picture, set a new password or send a password reset link, and more.
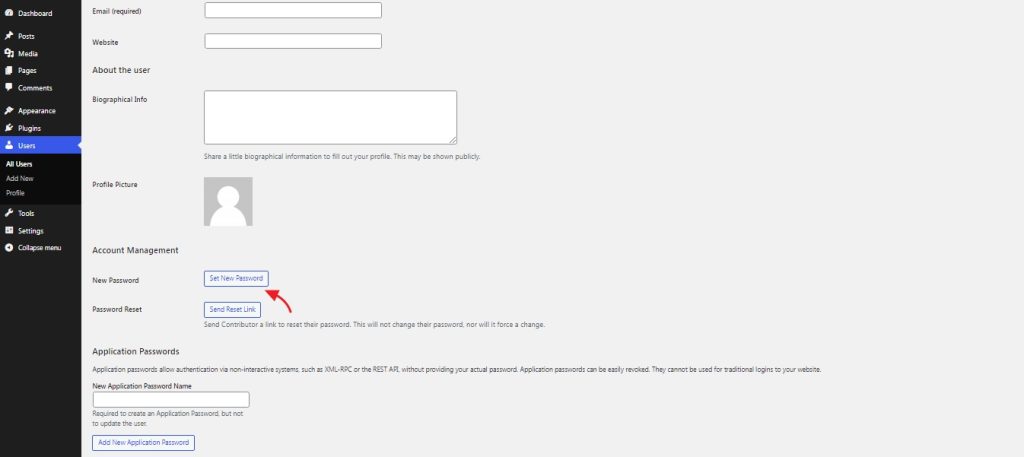
Once all the changes have been made, click on ‘Update User’.
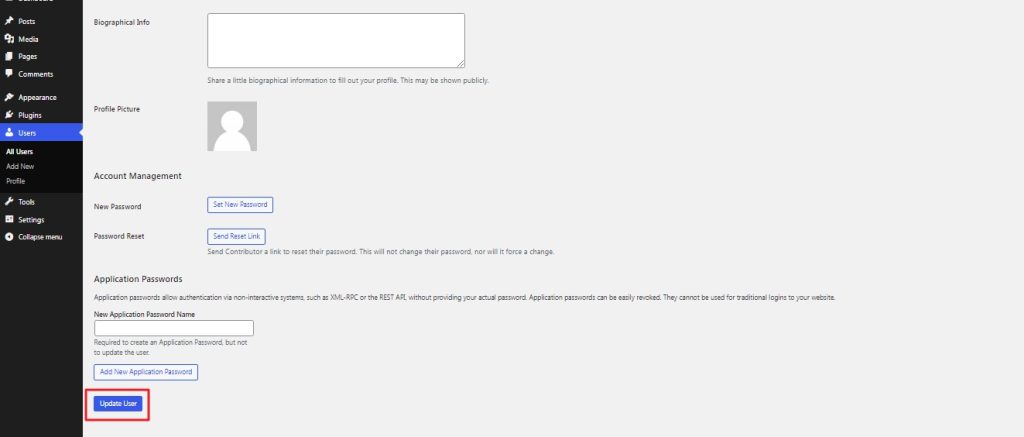
That’s all you need to do to manage and update the existing user roles in WordPress.
Also read: Complete Guide to Find & Fix Broken Links in WordPress
Wrapping Up
Knowing the various user roles and capabilities in WordPress is a must if you intend to provide dashboard access to multiple users.



